︎︎︎
Offshore Towers
New York, USA 2020
The
coast is a recursive environment for civilizations to thrive. Our ancestors
sought the coast for its resource abundance, from food to transportation,
presenting good trading opportunities that promoted development in strategic
coastal spots. The trend of coastal development has not changed; in any case,
it is accelerating. With an increasingly growing coastal population – expected
to increase by 1.66 billion people in 2050 –the current built-up area of cities
and the consequential anthropogenic effects, there is a niche to challenge our
built environment's standards along the shorelines.
Some
factors that contribute to the growth of coastal cities are the
following:
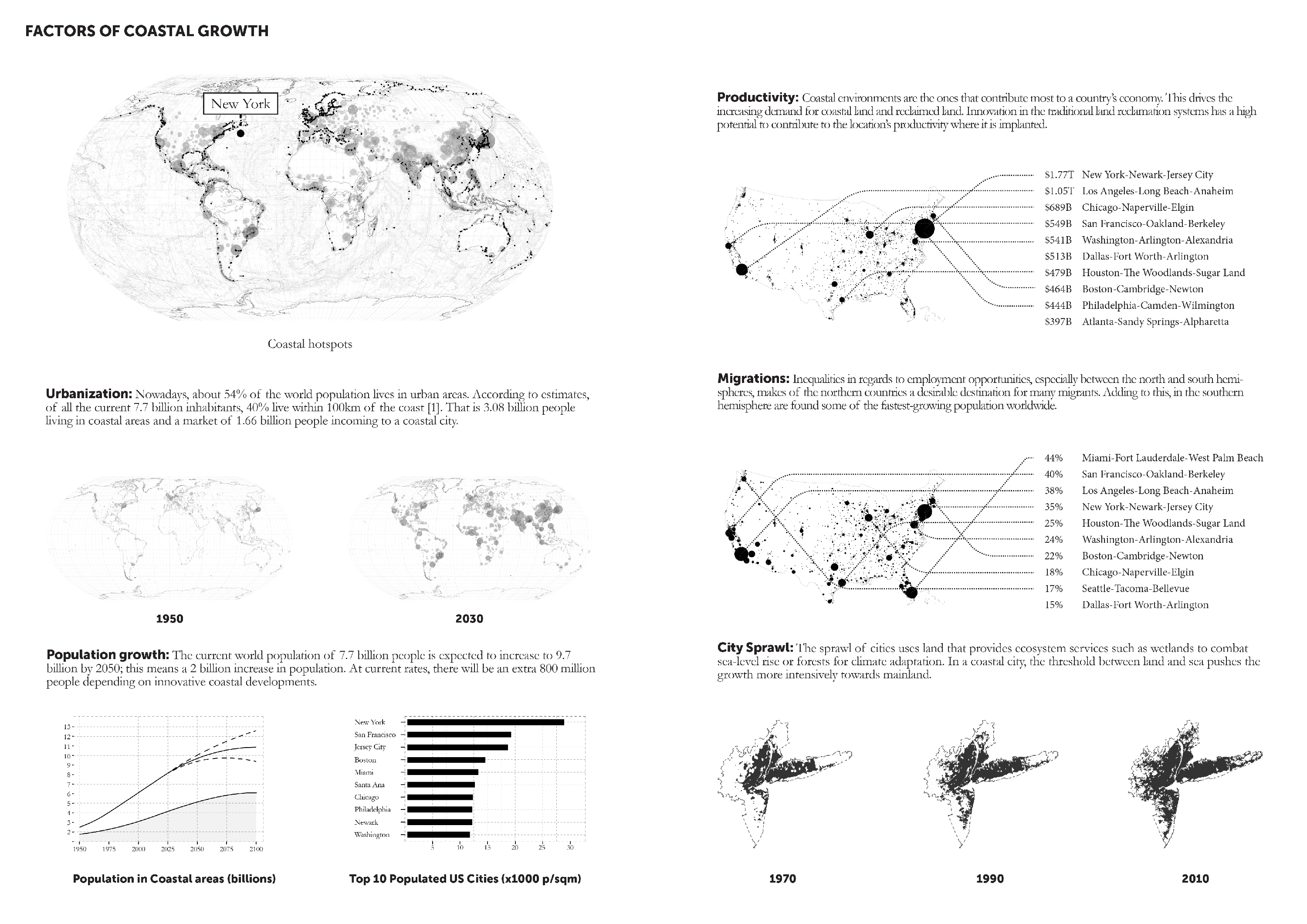
-Urbanization:
Nowadays, about 54% of the world population lives in urban areas. According to
estimates, of all the current 7.7 billion inhabitants, 40% live within 100km of
the coast. That is 3.08 billion people living in coastal areas and a
market of 1.66 billion people incoming to a coastal city.
-Population
growth: The current world population of 7.7 billion people is expected to
increase to 9.7 billion by 2050; this means a 2 billion increase in population.
At current rates, there will be an extra 800 million people depending
on innovative coastal developments.
-Productivity:
Coastal environments are the ones that contribute most to a country's economy.
This drives the increasing demand for coastal land and reclaimed land. Innovation
in the traditional land reclamation systems has a high potential to contribute
to the location's productivity where it is implanted.
-Migrations:
Inequalities in regards to employment opportunities, especially between the
north and south hemispheres, makes of the northern countries a desirable
destination for many migrants. Adding to this, in the southern hemisphere are
found some of the fastest-growing population worldwide.
-Tourism
industry: Worldwide, at 2016 levels, we were experiencing a tourism population
of over 1.2 billion visitors per year. Cities like New York itself hosts about
60 million visitors a year. This industry increases land demands to absorb this
temporal but constant population.
-City
Sprawl: The sprawl of cities uses land that provides ecosystem services such as
wetlands to combat sea-level rise or forests for climate adaptation. In a
coastal city, the threshold between land and sea pushes the growth more
intensively towards mainland.
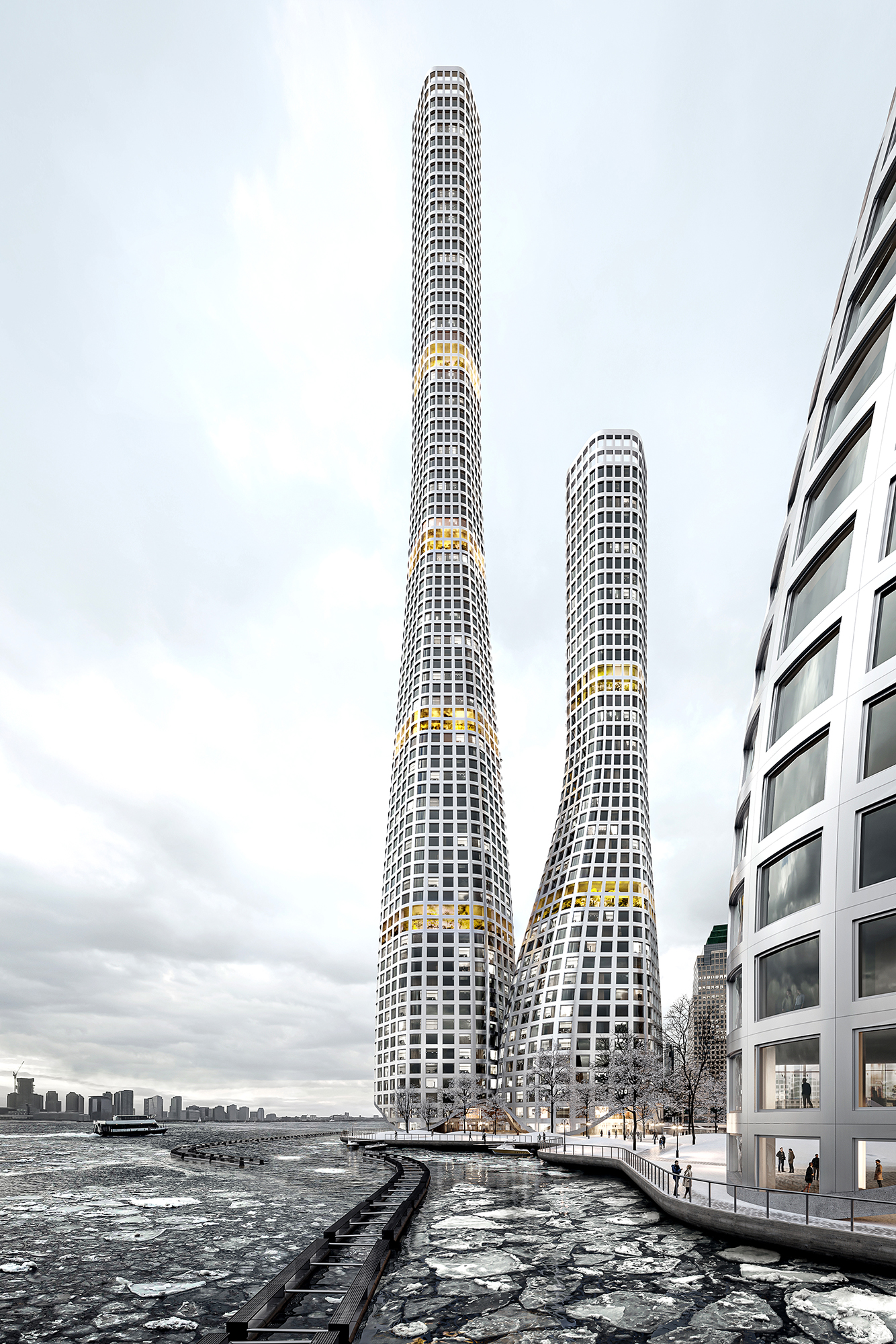
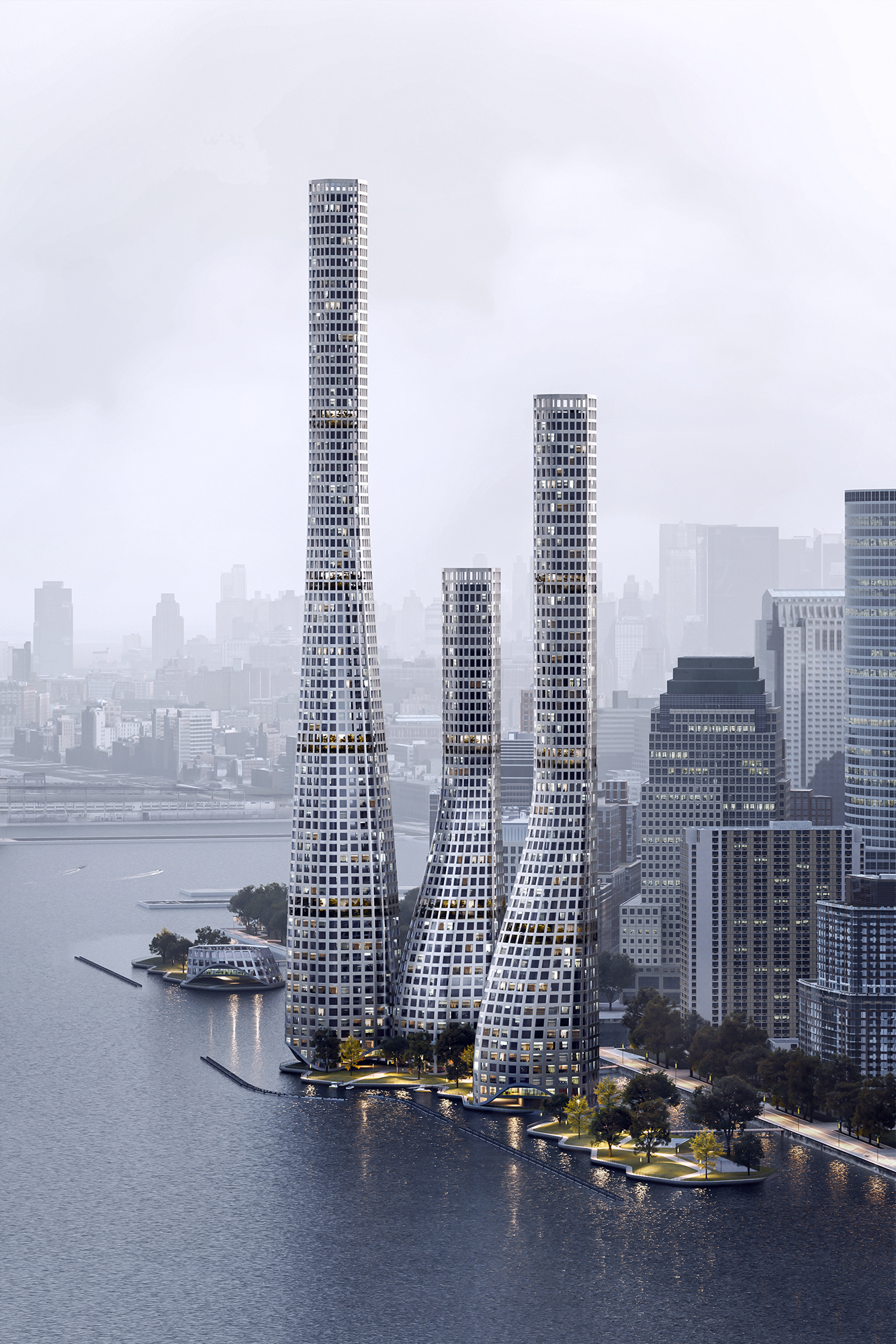
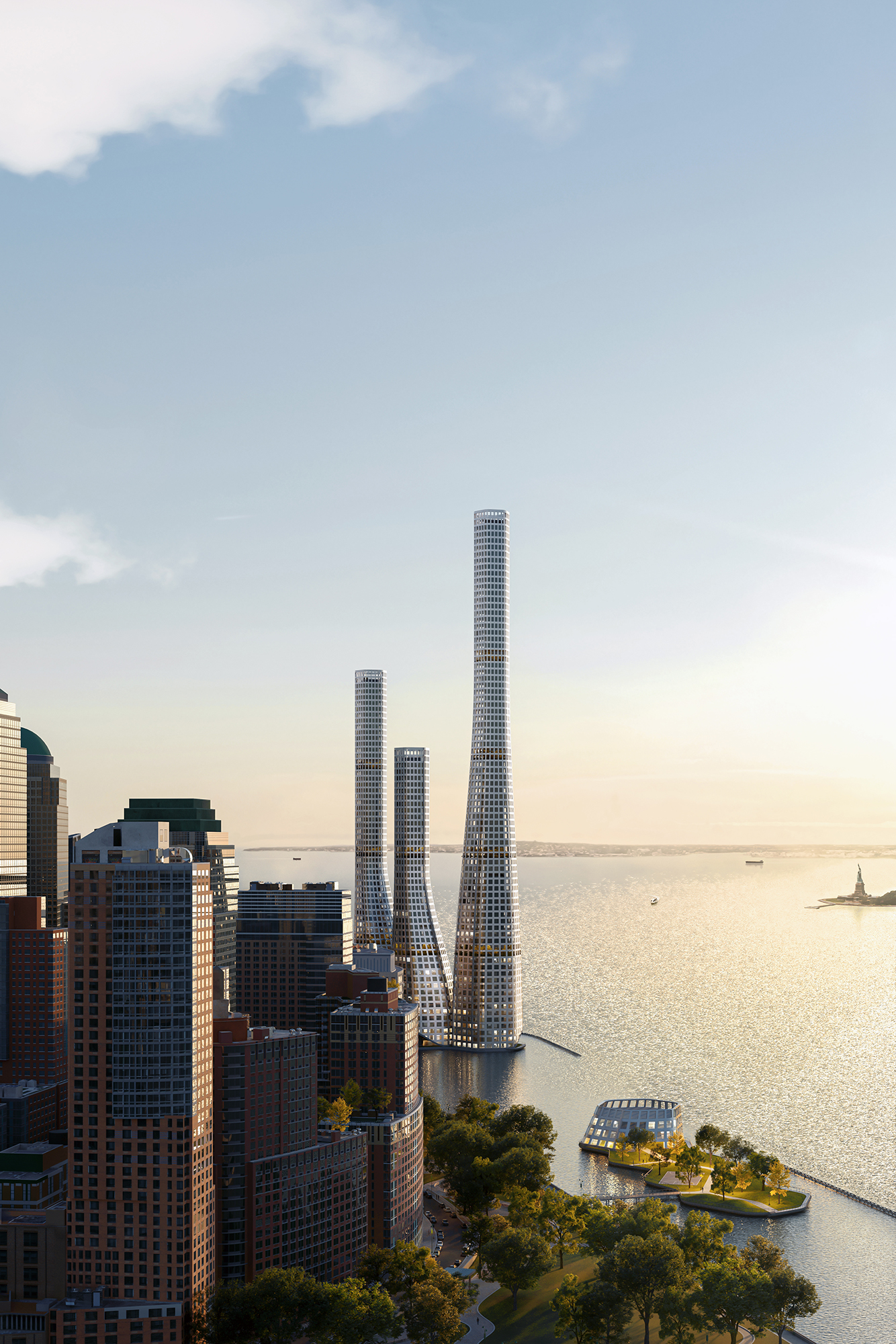
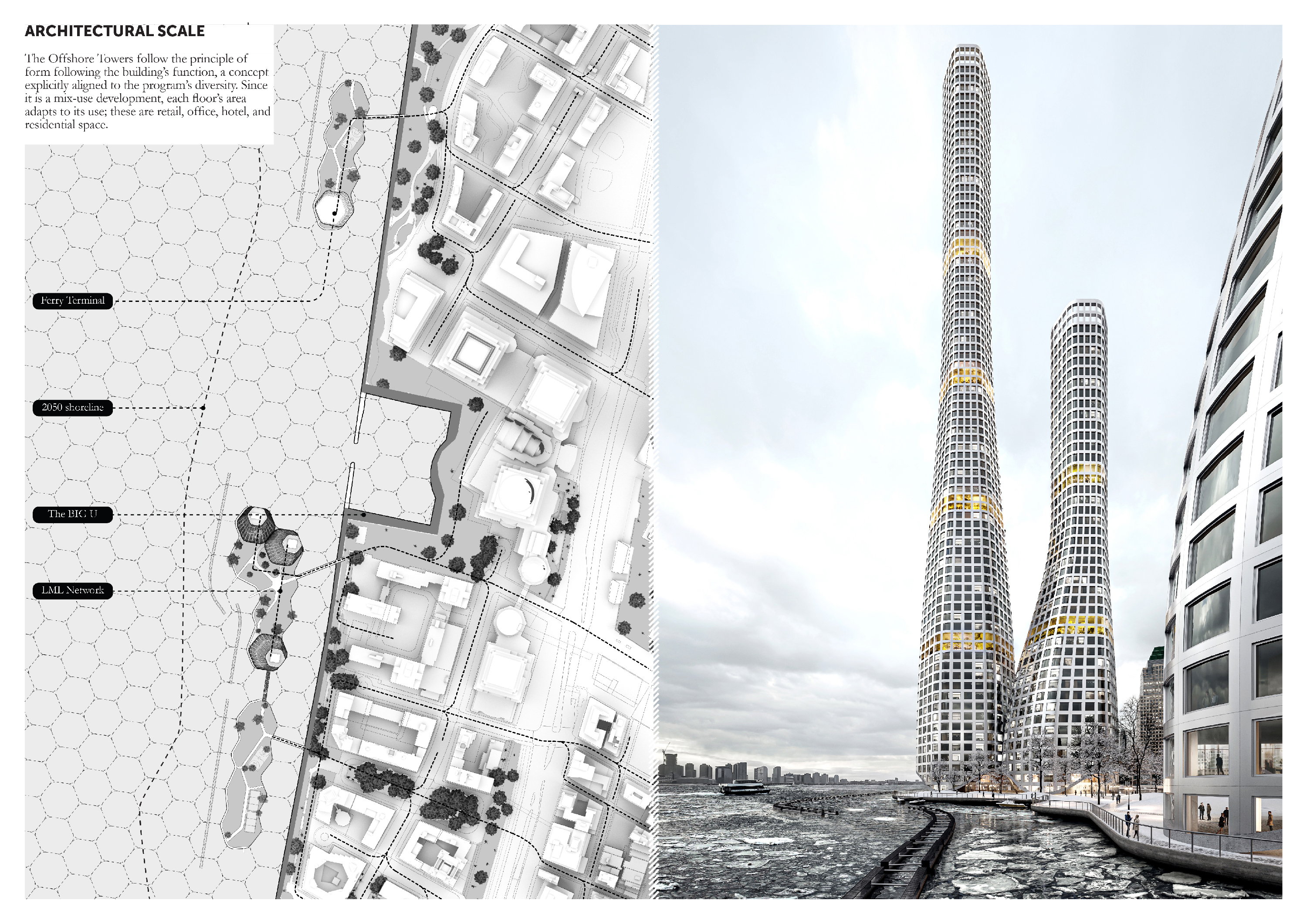
"The
Offshore Towers" is a water-based, mix-use development to adopt the
growing cultural, resiliency, and technological needs of Battery Park, New
York. The Offshore Towers seek to:
a)
reduce gentrification pressures of the ever-increasing technological industry
by building on newly created land.
b)
improve the local coastal resiliency with a new buffer zone
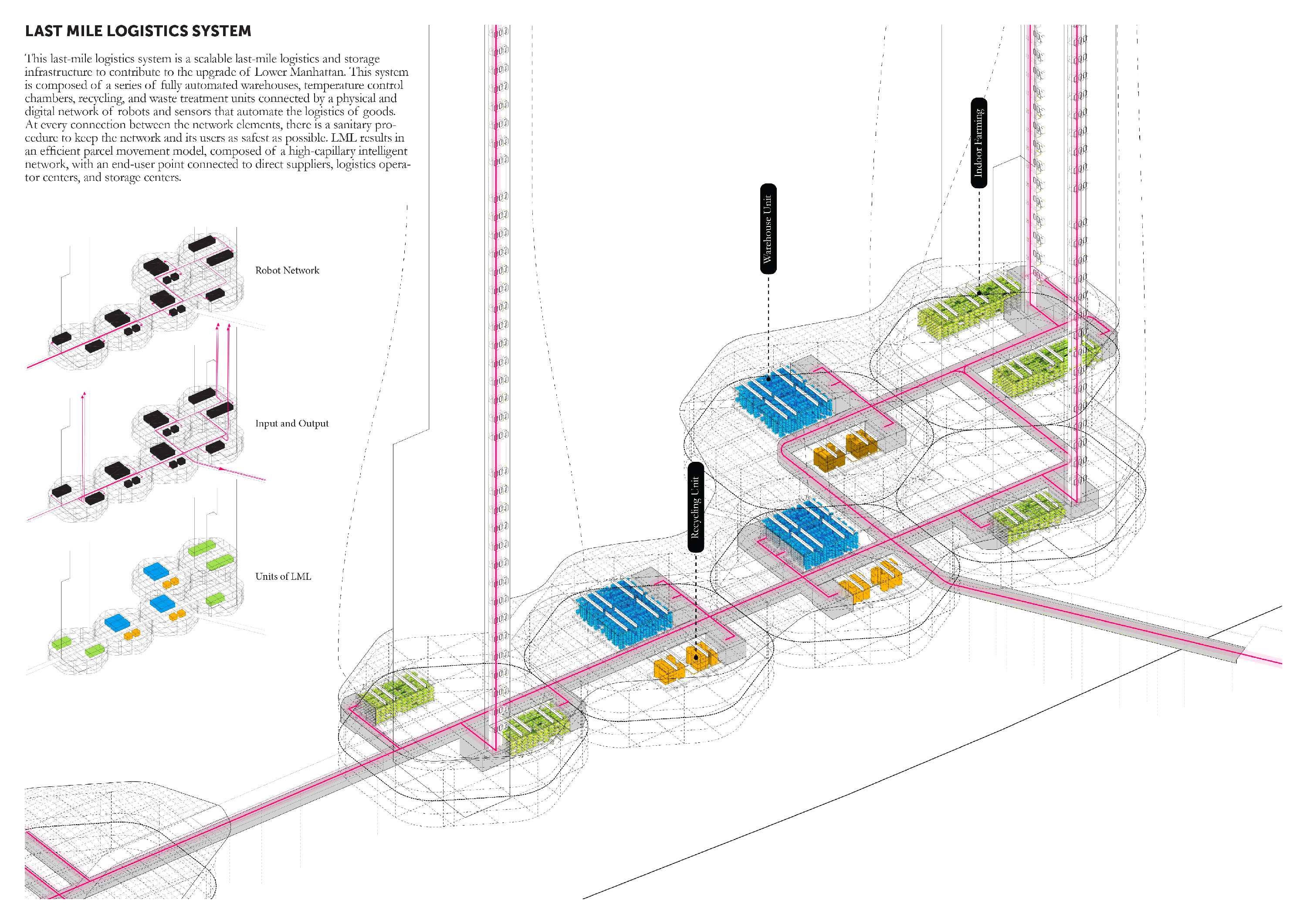
c)
improve logistics to the existing grid through the introduction of an automated
last-mile logistics network.
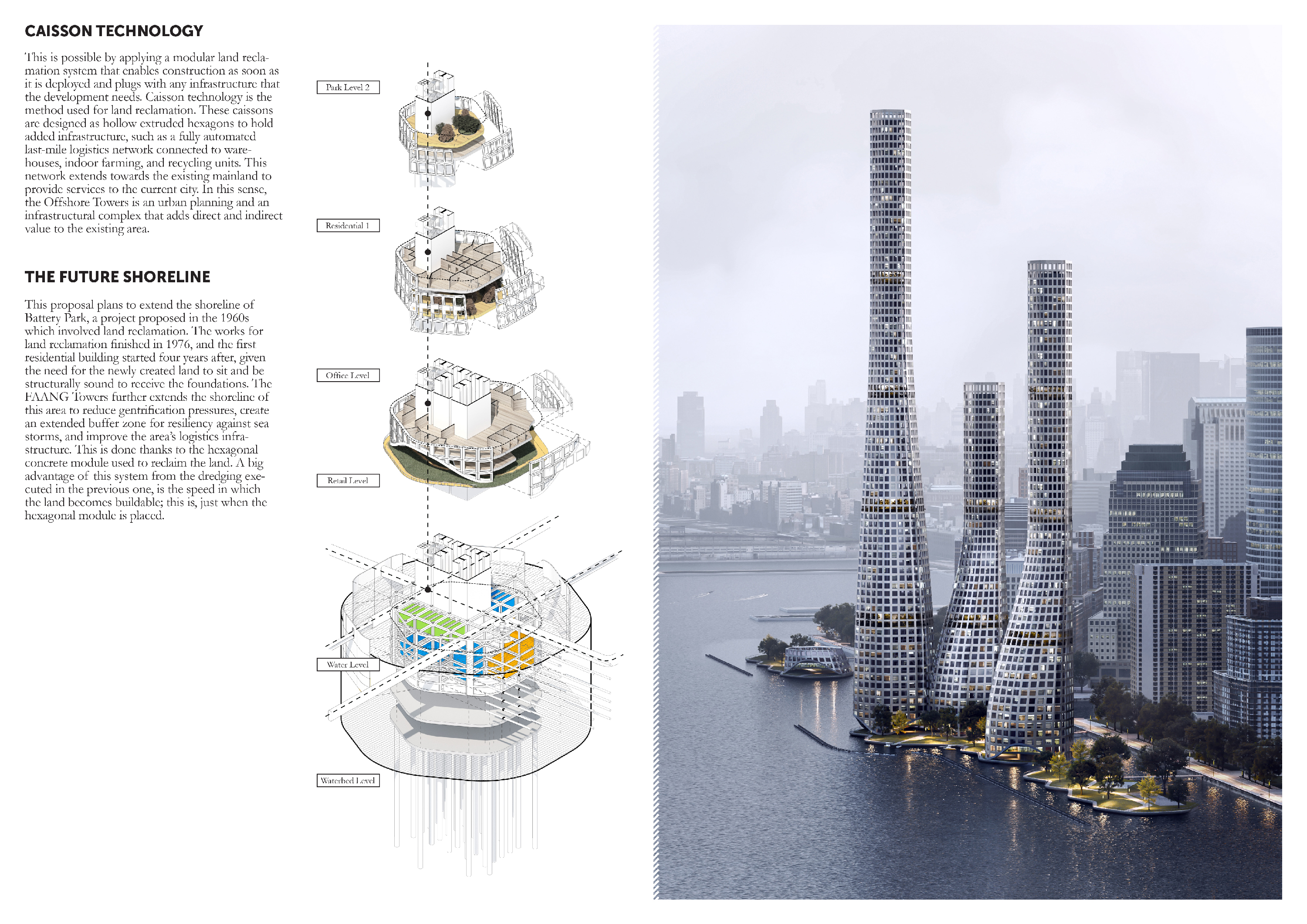
This is
possible by applying a modular land reclamation system that enables
construction as soon as it is deployed and plugs with any infrastructure that
the development needs. Caisson technology is the method used for land
reclamation. These caissons are designed as hollow extruded hexagons to hold
added infrastructure, such as a fully automated last-mile logistics network connected
to warehouses, indoor farming, and recycling units. This network extends
towards the existing mainland to provide services to the current city. In this
sense, the Offshore Towers is an urban planning and an infrastructural complex
that adds direct and indirect value to the existing area.
team: Pratik Borse, Gabriel Muñoz Moreno
location: Manhattan, New York.
year: 2020
program: office / masterplan / tower